Subclavian Steal Syndrome | The subclavian steal syndrome is a condition that results from the stenosis or occlusion of the subclavian artery proximal to the origin of the vertebral artery. Subclavian steal syndrome is a condition caused by retrograde blood flow in one or both vertebral arteries due to stenosis or occlusion of the proximal subclavian or innominate (brachiocephalic). Assessment | biopsychology | comparative | cognitive | developmental | language | individual differences | personality | philosophy | social | methods | statistics | clinical | educational | industrial | professional items | world psychology |. Subclavian steal syndrome affects the artery that supplies blood to the neck and head or the arteries that supply blood to the arms. After an adequate physical examination, routine laboratory studies should be ordered to address risk factors for atherosclerosis.
Subclavian steal syndrome (sss) is a condition in which the subclavian artery proximal to the origin of the vertebral artery narrows or becomes occluded, usually due to atherosclerosis. Subclavian steal syndrome affects the artery that supplies blood to the neck and head or the arteries that supply blood to the arms. Subclavian steal syndrome and subclavian steal phenomenon both result from severe proximal subclavian artery stenosis or occlusion resulting in retrograde flow in the ipsilateral vertebral artery. Subclavian steal syndrome, a form of peripheral artery disease (pad), is a set of symptoms caused by a blockage in one of the subclavian arteries, the large arteries that supply the arms. Subclavian steal syndrome is defined as stenosis or occlusion of the subclavian artery proximal to the origin of the vertebral artery, with consequent reversal of blood flow in the vertebral artery to.

Stenosis of the subclavian artery, proximal to the origin of the vertebral vessel, results in decreased perfusion pressure to the distal subclavian artery, leading to retrograde flow in the ipsilateral vertebral artery with exercise of the ipsilateral arm. Subclavian steal syndrome affects the artery that supplies blood to the neck and head or the arteries that supply blood to the arms. An arteriosclerotic stenotic plaque at the origin of the subclavian (proximal to the takeoff of the vertebral) allows enough blood. Subclavian steal may also occur in asymptomatic individuals. Subclavian steal syndrome is a disorder caused by reversed blood flow in one of the two major arteries that flow through the torso. The subclavian arteries are the large arteries which originate from the. Diseases related to subclavian steal syndrome via text searches within malacards or genecards suite drugs for subclavian steal syndrome (from drugbank, hmdb, dgidb, pharmgkb, iuphar. Subclavian steal syndrome is a rare condition causing syncope or neurological deficits when the blood supply to the affected arm is increased through exercise. Subclavian steal syndrome, a form of peripheral artery disease (pad), is a set of symptoms caused by a blockage in one of the subclavian arteries, the large arteries that supply the arms. Subclavian steal syndrome also referred to as subclavian steal phenomenon is a condition characterized by a reversal flow of the blood in the vertebral artery as a result of stenosis or occlusion. The proximal part of left subclavian is blocked on left side so no flow in vertebral and to left arm. Subclavian steal syndrome (sss) is a condition in which the subclavian artery proximal to the origin of the vertebral artery narrows or becomes occluded, usually due to atherosclerosis. Subclavian steal syndrome detected with d~plex pulsed doppler sonography.
The subclavian arteries are the large arteries which originate from the. Assessment | biopsychology | comparative | cognitive | developmental | language | individual differences | personality | philosophy | social | methods | statistics | clinical | educational | industrial | professional items | world psychology |. After an adequate physical examination, routine laboratory studies should be ordered to address risk factors for atherosclerosis. Subclavian steal syndrome, a form of peripheral artery disease (pad), is a set of symptoms caused by a blockage in one of the subclavian arteries, the large arteries that supply the arms. An arteriosclerotic stenotic plaque at the origin of the subclavian (proximal to the takeoff of the vertebral) allows enough blood.

Assessment | biopsychology | comparative | cognitive | developmental | language | individual differences | personality | philosophy | social | methods | statistics | clinical | educational | industrial | professional items | world psychology |. Subclavian steal syndrome occurs when narrowing/occlusion of the subclavian artery proximal to the origin of the vertebral artery causes a reversal of blood flow in the ipsilateral vertebral artery to. The subclavian arteries are the large arteries which originate from the. Subclavian steal may also occur in asymptomatic individuals. Subclavian steal syndrome is a disorder caused by reversed blood flow in one of the two major arteries that flow through the torso. Subclavian steal syndrome, a form of peripheral artery disease (pad), is a set of symptoms caused by a blockage in one of the subclavian arteries, the large arteries that supply the arms. The proximal part of left subclavian is blocked on left side so no flow in vertebral and to left arm. The term subclavian steal describes retrograde blood flow in the vertebral artery associated with proximal ipsilateral subclavian artery. In the evaluation of the extracranial carotid circulation for occlusive. These tests should include a. Subclavian steal syndrome implies the presence of significant symptoms due to arterial insufficiency in the brain (ie, vertebrobasilar insufficiency) or upper extremity. Subclavian steal syndrome is defined as stenosis or occlusion of the subclavian artery proximal to the origin of the vertebral artery, with consequent reversal of blood flow in the vertebral artery to. Subclavian steal syndrome is rare, but sometimes difficult to diagnose.
The subclavian arteries are the large arteries which originate from the. Because of this, people may experience symptoms in these areas. Subclavian steal syndrome is a disorder caused by reversed blood flow in one of the two major arteries that flow through the torso. Blood from right vertebral enters left vertebral and flows back to supply left. Subclavian steal syndrome is said to be present when the blood flow in vertebral artery reverses due to significant stenosis or occlusion of the ipsilateral subclavian artery just before the origin of the.
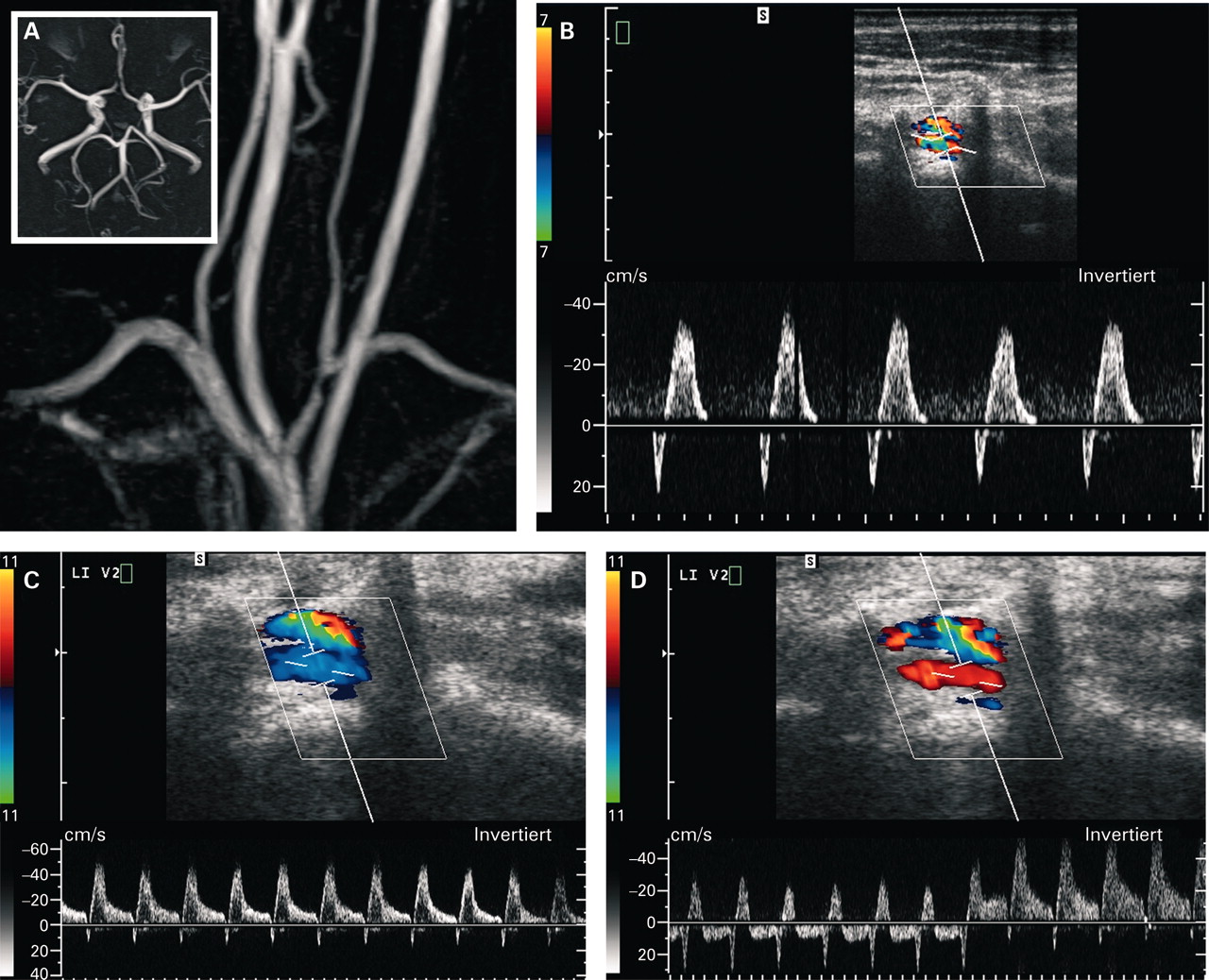
Subclavian steal syndrome occurs when narrowing/occlusion of the subclavian artery proximal to the origin of the vertebral artery causes a reversal of blood flow in the ipsilateral vertebral artery to. In the evaluation of the extracranial carotid circulation for occlusive. Subclavian steal may also occur in asymptomatic individuals. Assessment | biopsychology | comparative | cognitive | developmental | language | individual differences | personality | philosophy | social | methods | statistics | clinical | educational | industrial | professional items | world psychology |. Subclavian steal syndrome is a rare condition causing syncope or neurological deficits when the blood supply to the affected arm is increased through exercise. The subclavian steal syndrome is a condition that results from the stenosis or occlusion of the subclavian artery proximal to the origin of the vertebral artery. These tests should include a. Diseases related to subclavian steal syndrome via text searches within malacards or genecards suite drugs for subclavian steal syndrome (from drugbank, hmdb, dgidb, pharmgkb, iuphar. The term subclavian steal describes retrograde blood flow in the vertebral artery associated with proximal ipsilateral subclavian artery. Subclavian steal syndrome and subclavian steal phenomenon both result from severe proximal subclavian artery stenosis or occlusion resulting in retrograde flow in the ipsilateral vertebral artery. Subclavian steal syndrome (sss) is a condition in which the subclavian artery proximal to the origin of the vertebral artery narrows or becomes occluded, usually due to atherosclerosis. Subclavian steal syndrome detected with d~plex pulsed doppler sonography. Stenosis of the subclavian artery, proximal to the origin of the vertebral vessel, results in decreased perfusion pressure to the distal subclavian artery, leading to retrograde flow in the ipsilateral vertebral artery with exercise of the ipsilateral arm.
Subclavian Steal Syndrome: The subclavian arteries are the large arteries which originate from the.
Referanse: Subclavian Steal Syndrome
0 Tanggapan:
Post a Comment